| Version 32 (modified by , 15 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
How-To Test GRASS6 ¶
Scope of this page ¶
This pages is intended to users and developers who want to test a GRASS installation (test protocol). As side effect, you can also showcase GRASS 6 using these commands.
Note: see here for a first time user's mini-intro.
Table of Contents
- Scope of this page
- Requirements
- Start of the program
- Re-launch of GUI from command line
- Using gis.m TclTk graphical user interface
- Using wxPython graphical user interface (wxGUI)
- Display various maps in a classic GRASS X-monitor
- 3D visualization with NVIZ
- Simple raster analysis
- Simple vector analysis
- Using QGIS' GRASS toolbox
- See Also
Requirements ¶
- GRASS 6 installation (source code and binaries download)
- Educational data set: OSGeo Educational data set North Carolina: data and description.
Extract the NC sample data set for GRASS:
mkdir $HOME/grassdata tar xvfz nc_spm_latest.tar.gz
Start of the program ¶
GRASS 6 is started either from the menu (if installed therein) or from command line. In all cases, select mapset "user1".
# show available options grass64 --help
Expected result: the help text should be shown.
# start with current Tcl/Tk based graphical user interface (gis.m) grass64 -tcltk # start with wxPython based graphical user interface grass64 -wxpython
Expected result: the selected graphical user interface should come up.
# start with text based interface grass64 -text
Expected result: the text user interface should come up.
Re-launch of GUI from command line ¶
# start with current Tcl/Tk based graphical user interface (gis.m) g.gui tcltk # start with wxPython based graphical user interface g.gui wxpython
Expected result: the selected graphical user interface should come up.
Using gis.m TclTk graphical user interface ¶
- To add a raster map, click in GIS manager on "Add raster layer" button,
- Click on word "raster1" which appears in the canvas to enable in the lower part the raster map tool (should already be there)
- In "Display raster maps", select "Base map" button, explode "PERMANENT" mapset, and select map "elevation" (click ok or use double click on map name)
- The map name should have appeared in canvas
- Get second "Map Display 1" window on top, therein click on "Display active layer" button (most left): it should display the elevation map.
- Try to zoom (open with left mouse button a zoom box)
- Create a profile ("Create profile" button)
- In "Profile window" tool, use left button to select raster map gaina ("elevation" in PERMANENT)
- Click "Draw profile transect" to draw a transect in the main map window
- Click "Draw profile" button to draw it. Each transect turn is indicated as vertical line in the profile.
- To add a vector map, click on the "Add vector layer" button
- Click on word "vector1" which appears in the canvas to enable in the lower part the vector map tool (should already be there)
- In "Display vector maps", select "Vector map" button, explode "PERMANENT" mapset, and select map "roadsmajor" (click ok or use double click on map name)
- The map name should have appeared in canvas
- Get second "Map Display 1" window on top, therein click on "Display active layer" button (most left): it should display the elevation map.
Expected result: it should just work.
Using wxPython graphical user interface (wxGUI) ¶
Basic map display ¶
- Click in Layer manager on "Add raster map layer" button,
- select raster map "elevation@PERMANENT" in properties dialog and click "OK",
- right mouse click in layer tree and choose from contextual menu "Zoom to selected map(s)", map should appear in canvas.
- Try to zoom, to create a profile etc.
Expected result: it should just work.
Digitizing ¶
- In the Layer manager click on "Add raster map layer" button,
- select raster map "elev_lid792_1m@PERMANENT" in properties dialog and click "OK",
- right mouse click in layer tree and choose from contextual menu "Zoom to selected map(s)", map should appear in canvas.
- In the Layer manager click on "Add raster map layer" button again,
- select raster map "ortho_2001_t792_1m@PERMANENT" in properties dialog and click "OK".
- Zoom to houses within the map, zoom one house,
- on the right-hand end of the map canvas window select "Digitize" from the pull-down list (originally set to "2D view"),
- go to "Select vector map" -> "New vector map", enter "house" as vector map name, "OK".
- Go into the Layer Manager and click the "Show attribute table" icon,
- therein go into the "Manage tables" tab and add a new column "name" as varchar type with length 50. Then "Add", then "Quit" to close the Attribute Manager.
- Now digitize a boundary around the house and a centroid, for both enter "my home" as "name" attribute.
- Leave the digitizer by going back to "2D view". The house polygon should show up as grey area.
Expected result: it should just work.
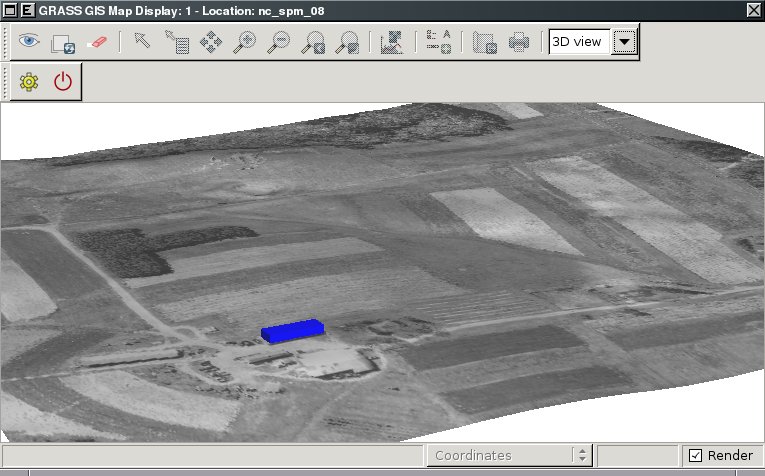
Extrude 2D vector to 3D vector ¶
- Go in the Layer Manager to "Vector" -> "Develop vector map" -> "Extrude 3D vector map".
- Have the "house" vector map selected, insert "house3d" as new 3D vector map (Required tab),
- go to "Optional" tab and activate "Trace elevation" to make the house bottom line follow the terrain and select "elev_lid792_1m@PERMANENT" as "Elevation map", and a "Height" of 5 (meters),
- check "Add created map into layer tree" and then "Run". This creates the 3D house vector block, add it to the map canvas and display the map.
Expected result: it should just work.
Display 3D house ¶
- Click in Layer manager on "Add raster map" button,
- select raster map "elev_lid792_1m@PERMANENT" in properties dialog and click "OK",
- right mouse click in layer tree and choose from contextual menu "Zoom to selected map", map should appear in canvas,
- select vector map "house3D@PERMANENT" in properties dialog and click "OK",
- from Map Display toolbar choose "3D view",
- move the puck to change the viewpoint in "3D View Tools" window (tab "View"),
- increase the raster resolution in "Visualize" -> "Raster surfaces" -> "Resolution fine" to 1 (the smaller the number, the higher the resolution).
Expected result: it should just work.
Display various maps in a classic GRASS X-monitor ¶
(NOTE: not for native winGRASS, but for Cygwin-winGRASS and Unix compliant installations)
As first step on the command line we set the current region to extent and resolution of the elevation raster map. Then we open a graphical map display ("GRASS monitor") and display the map:
g.region rast=elevation -p d.mon x0 d.rast elevation d.vect roadsmajor
Expected result: GRASS monitor should open and show the selected maps
Display as shaded terrain map:
d.his i=elevation_shade h=elevation d.vect roadsmajor # set barscale position per mouse click into map: d.barscale -mt
3D visualization with NVIZ ¶
# raster map and 2D vector lines map nviz elevation vect=roadsmajor
# raster map and 2D vector lines map and 3D vector points nviz elevation vect=roadsmajor points=precip_30ynormals_3d
Tests: navigate with the puck, interrogate map, etc. (ADD MORE)
Expected result: should not crash at all but show maps as expected
- You can also start Tcl/Tk NVIZ from the File menu. It respects the current computational region. (g.region -p)
Simple raster analysis ¶
Raster analysis comprises a lot of functionality.
Raster algebra ¶
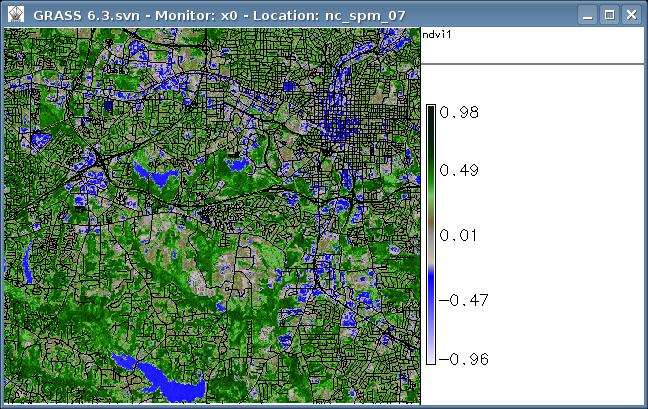
Normalized Differences Vegetation Index (NDVI) from LANDSAT-TM7:
# set current region/resolution to map: g.region rast=lsat7_2002_40 -p # display metadata: r.info -h lsat7_2002_40 # generate NDVI: r.mapcalc "ndvi = 1.0 * (lsat7_2002_40 - lsat7_2002_30) / (lsat7_2002_40+ lsat7_2002_30)" r.info -r ndvi r.colors ndvi color=ndvi # display 2D: d.mon x0 # MS Window users: use the display manager instead d.rast.leg ndvi d.vect streets_wake # display 3D: nviz elevation col=ndvi vect=streets_wake
Expected results: the NDVI map should be colorized in near natural colors, see screenshot:
Raster statistics ¶
Univariate statistics:
r.univar ndvi
Expected results: minimum: -0.956522, maximum: 0.978723, mean: 0.190006 etc.
Simple vector analysis ¶
- TODO
Extracting from vector maps ¶
- extract large streets from "streets_wake"
SQL support ¶
g.region vect=schools_wake -p d.erase # MS Window users: use the display manager instead # show all schools in Wake County d.vect schools_wake col=red icon=basic/circle siz=5 # show a subset of all elementary schools in Raleigh d.vect schools_wake where="ADDRCITY='Raleigh' and GLEVEL='E'"
Vector statistics ¶
Univariate statistics:
# show available columns v.info -c precip_30ynormals_3d v.univar precip_30ynormals_3d col=annual type=point
Expected result: mean: 1289.31 etc.
Transfer raster slope to vector segments ¶
- v.split, v.to.db
Shortest path routing ¶
- NC bus routes... map "busroutesall"
Using QGIS' GRASS toolbox ¶
Start "qgis" within GRASS shell.
- Go menu "Plugins, Pluginmanager, activate "GRASS plugin", OK button: a set of new buttons should appear
- click "Add GRASS raster layer" button, select "elevation" map
- click "Add GRASS raster layer" button, select "elevation_shade" map
- click right mouse button in legend on "elevation_shade" map, move transparency to 40%
- click "Add GRASS vector layer" button, select "roadsmajor" map, select layer "1-line" (level 1 is the topological level), OK
See Also ¶
The following demos are related to the GRASS book, 3rd edition 2008 (based on NC data set):
(NOTE: not all for native winGRASS, but for Cygwin-winGRASS and Unix compliant installations. For native WinGRASS use the GUI instead of d.* commands)
Attachments (5)
-
nc_ndvi.jpg
(99.4 KB
) - added by 17 years ago.
North Carolina Raleight NDVI from Landsat
-
grass64_wx_start.png
(165.5 KB
) - added by 16 years ago.
screenshot
-
grass64_text_start.png
(56.1 KB
) - added by 16 years ago.
text startup
-
grass64_digitize.jpg
(58.6 KB
) - added by 15 years ago.
wxGUI digitizer (house)
-
grass64_nviz_3dhouse.jpg
(70.8 KB
) - added by 15 years ago.
wxGUI 3D view mode
Download all attachments as: .zip