| Version 1 (modified by , 16 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
ADAGUC netCDF - * CURRENTLY UNDER CONSTRUCTION *
The ADAGUC netCDF driver reads and writes files which comply with the ADAGUC Data Products Standard (ADAGUC website). ADAGUC files are created by using the NetCDF4 API. The NetCDF4 API has the ability to store files in the HDF5 file format while remaining backwards compatible with previous versions of netCDF. The ADAGUC driver supports the creation of NetCDF3 and NetCDF4 files. In NetCDF3 mode the driver writes NetCDF files, in NetCDF4 mode the driver writes HDF5 files. ADAGUC netCDF files follow the Climate and Forecast (CF) 1.2 and ISO:19115 metadata conventions. Besides these conventions the format provides space for specific product metadata.
The file structure
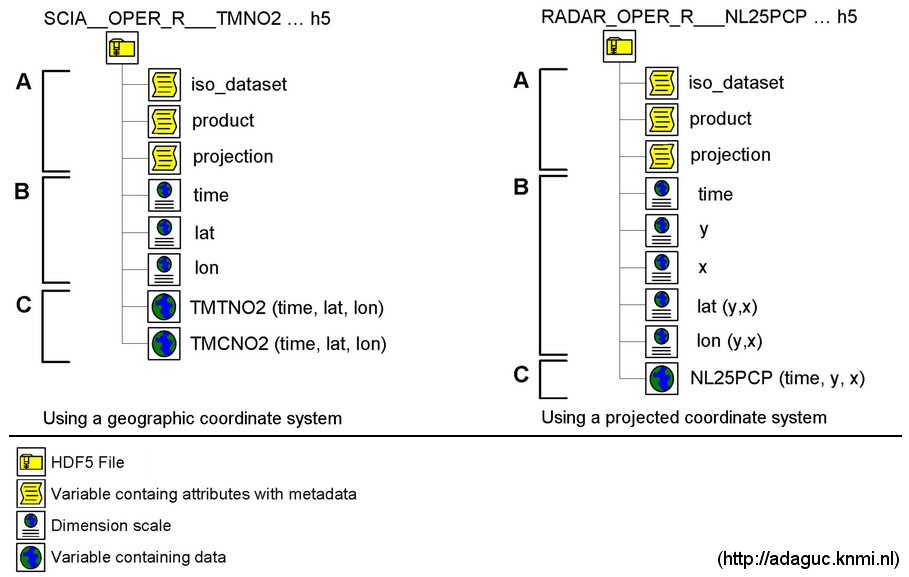
The ADAGUC internal file structure contains variables which can be subdivided in three types: variables to store the metadata, variables to store the dimension scales and variables to store the data. A schematic overview of the ADAGUC file structure for the different types is given in the figure below. The three types of variables (metadata, dimension scales and data) are indicated with A, B and C respectively.
(A) Metadata - Metadata is stored in attributes which are assigned to a variable. The variables ‘product’, ‘iso_dataset’ and ‘projection’ are used to store the metadata.
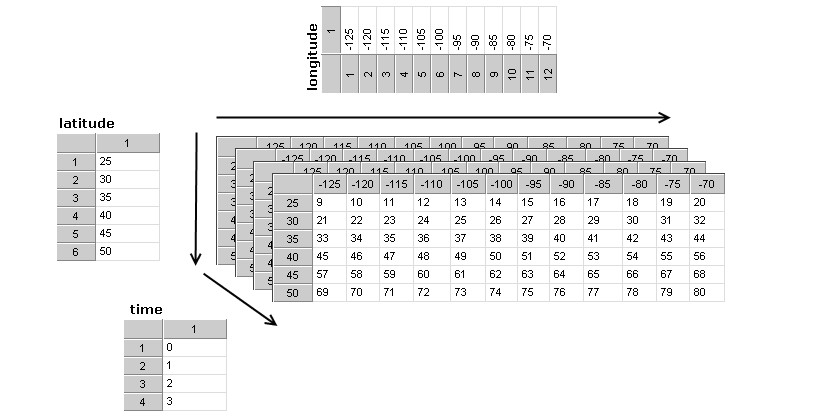
(B) Dimension scales - Dimension scales are used as coordinate variables and time intervals. They provide information about geolocation and time to the data variables. The dimension scales follow the NetCDF Climate and Forecast (CF) Metadata Conventions. Dimension scales are lists containing coordinates or time intervals. The figure below shows geographic raster data with the dimensions time, lat and lon. Its size is, in this example, 4x6x12. This means that there are 4 indexes for time, 6 for latitude and 12 for longitude. According to the CF conventions the dimensions should have the order time, lat, lon.
In case the raster data uses a geographic coordinate system, the required dimensions are time, lat and lon which represent the center of the pixel. When the raster data is projected the dimension scales x and y are included which represent the projected coordinates. The dimension scales lat and lon become a function of y and x (see the right part of the file structure), providing the latitude and longitude at the location of y and x, respectively. In this case y and x contain the projected coordinates, while lat and lon represent the geographic latitudes and longitudes in degrees at location y, x. For detailed information see the CF Conventions.
(C) Data - This part contains the data in the file structure. The data is stored in variables which are functions of the dimension scales. For geographic raster data the variable is a function of time, lat and lon. For projected raster data the variable is a function of time, y and x, as can be seen in the illustration of the file structure. The ADAGUC format currently supports X, Y and time dimensions, stored as dimension scales in the file according the CF Conventions. The driver supports two ways of time sub-setting. The first is by making selections in time by choosing band numbers, the second is by providing the time in the file name. By using gdalinfo on the ADAGUC file the available band numbers and dimensions are listed. With this information a subset can be read with for example: gdalinfo ADAGUC:thefile.nc:variable:time=20
GDAL Creation options
Creation options can be used to provide additional metadata and set the behavior of the driver. Metadata attributes set as a creation option override already existing metadata attributes.
METANCML – It is possible to provide additional metadata which is stored in an NcML XML file. The attributes from the groups product, iso_dataset, projection and custom are copied. When the name of the dataset is specified in the product::variables attribute, specific dataset attributes can be placed under the group with the name of the dataset. For example: -co “METANCML=NcMLMetadataFile.xml”
FORCENC3 – When set to true, the NetCDF4 driver writes in NetCDF3 mode. When unspecified the value is FALSE, in this case the driver writes in NetCDF4 mode. For example: -co “FORCENC3=TRUE”
VALSTART and VALSTOP – Overwrites the product validity_start and product validity_stop attributes in the product group. For example: –co “VALSTART=20080921T101900”
DATASETNAME - Specifies the name of the dataset
LONGNAME, STDNAME and UNITS – Sets the long_name, standard_name and units attributes of the dataset.
NAN – Sets the no data value of the dataset. The _FillValue attribute of the dataset is filled with the NAN number.
Building the driver
The ADAGUC netCDF driver requires at least the netCDF-4.0, HDF-1.8.1 and UDUNITS-1 packages to be installed.
- netCDF library
- HDF5 library
- http://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/udunits/udunits-1/index.html Unidata units library]
To make sure that the libraries are found during the compilation process you can use configure LIBS="-lhdf5 -lhdf5_hl -ludunits $LIBS". Use --with-netcdf=<path to install tree> to build GDAL with the NetCDF library.
Attachments (7)
- ADAGUC_raster_file_structure_small.jpg (82.1 KB ) - added by 16 years ago.
- ADAGUC_NetCDF_dimension_scales.jpg (61.0 KB ) - added by 16 years ago.
- GDAL_ADAGUC_source_v0.1.tar.gz (25.9 KB ) - added by 16 years ago.
- GDAL_ADAGUC_source_v0.2.tar.gz (27.5 KB ) - added by 16 years ago.
- OGR_ADAGUC_SOURCE_v0.1.tar.gz (5.8 KB ) - added by 15 years ago.
- OGR_ADAGUC_SOURCE_v0.2.tar.gz (7.5 KB ) - added by 15 years ago.
- GDAL_ADAGUC_source_v0.3.tar.gz (27.8 KB ) - added by 14 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip